
How to Fix Potassium Deficiency in Cannabis
Growing the best weed crop possible is up there with the most satisfying things of all time, especially for those of us who have really caught the ganga-growing bug. But to say it comes with a couple of key challenges would be a slight understatement.
Who knew that growing a plant literally called weed could, at times, be so hard?
From getting the environmental factors dialed in, to battling pests and diseases, to making sure you’re feeding your plants the right amount of macro and micronutrients. There’s a lot to keep track of. And that last one often trips up newer growers.
Potassium is one of the three main macronutrients that cannabis needs to thrive, along with nitrogen and phosphorus. It plays a crucial role in plant growth and development by aiding in photosynthesis, water regulation, and protein synthesis.
Why do cannabis plants need potassium?
Potassium is a vital, mobile macronutrient that plays a crucial role in a huge range of weed plant functions.
First up, it helps regulate the opening and closing of stomata. The stomata are the microscopic pores on the underside of your plant’s leaves, responsible for gas exchange. Without enough potassium, these pores won’t open and close properly, leading to reduced photosynthesis and growth.
Potassium is also vital for protein synthesis, which is essential for plant growth and development. It helps produce enzymes that facilitate the conversion of nitrogen into amino acids, which then form proteins.
It is also:
- Encourages early growth.
- Enhances frost resistance
- Helps the plant effectively transport water (and other nutrients) throughout the whole plant.
- Improves your crop’s quality.
- Boosts the rooting process.
- Increases bud quality, density, and development.
What are the symptoms of potassium deficiency in cannabis plants?
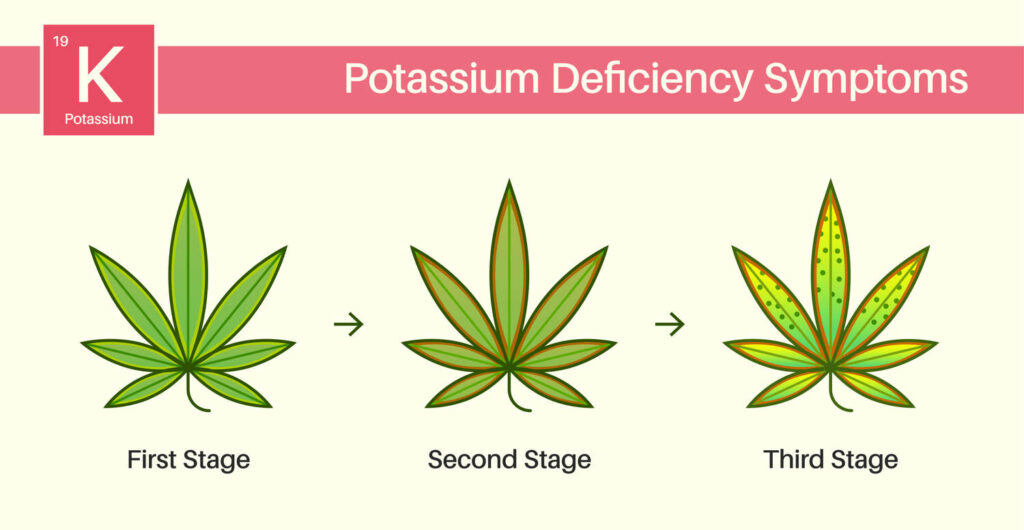
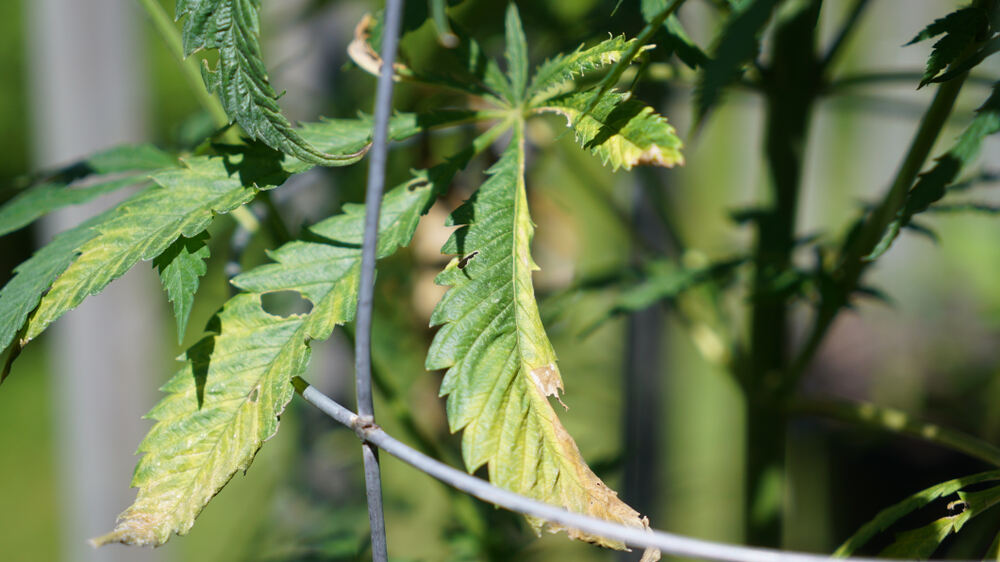
Identifying potassium deficiency early can save your plants. Here are the key symptoms to look out for:
- Yellowing Leaves: Older leaves may start to yellow at the edges and tips, although this could be confused with calcium deficiency – the thing to remember is potassium deficiency affects the edges of the leaves first.
- Brown Spots: Look for brown or burnt spots on the leaves, typically starting at the edges.
- Weak Stems: The stems may become weak and brittle.
- Slow Growth: Overall growth may be stunted, and the flowering phase may be delayed.
What are the main causes of cannabis potassium deficiency?
Potassium deficiency can be caused by a range of factors, the most common being:
- Poor Soil Quality: Soil lacking in organic matter or nutrients.
- Incorrect nutrient feeding: Under or overfeeding with potassium-rich fertilizers.
- Improper pH levels: A pH level that is too high or too low can hinder potassium absorption. Soil growers need to keep the pH at 6.0 to 7.0, while 5.5 to 6.5 is ideal for hydro/coco-grown plants.
- Overwatering: Excess water can wash away nutrients, including potassium.
- Nutrient Lockout: An imbalance of other nutrients can lock out potassium, making it unavailable to the plant.
How to treat potassium deficiency in cannabis plants?
Potassium, like nitrogen and phosphorus, is a mobile nutrient. When the plant realizes that it isn’t getting enough potassium from the root system, it can grab some of the stored potassium stored in the older fan leaves and move it to the newer growth.
This is why potassium deficiency signs often first appear on older leaves, and why taking action early is essential.
To treat a potassium deficiency in your cannabis plants:
- Check pH levels: Ensure the soil pH is between 6.0 and 7.0 for soil, or 5.5 to 6.5 for hydro/coco. Use a pH meter to adjust as necessary.
- Add potassium-rich fertilizers: Use fertilizers like potassium sulfate or organic options (kelp meal and wood ash are both great options). Be careful not to over feed though!
- Proper watering practices: Avoid overwatering, and make sure your soil has good drainage. You want about 25% of the water you give to drain out each time you water/feed.
- Flush the soil: If nutrient lockout is suspected, flush the soil with pH-balanced water to remove excess salts and other nutrients.
- Monitor plant health: Keep an eye on your plants for signs of improvement. This may take a week or so.
All growers need a pH meter, no matter what medium you are growing in.
If you are using hydro/coco growing methods, you will need to grab an EC or TDS meter to measure your nutrient strength. Without one of these two tools, there is really no accurate way to measure the strength of your solution. Soil growers can also benefit from an EC or TDS meter when growing with liquid nutrients.
How to prevent cannabis potassium deficiency?
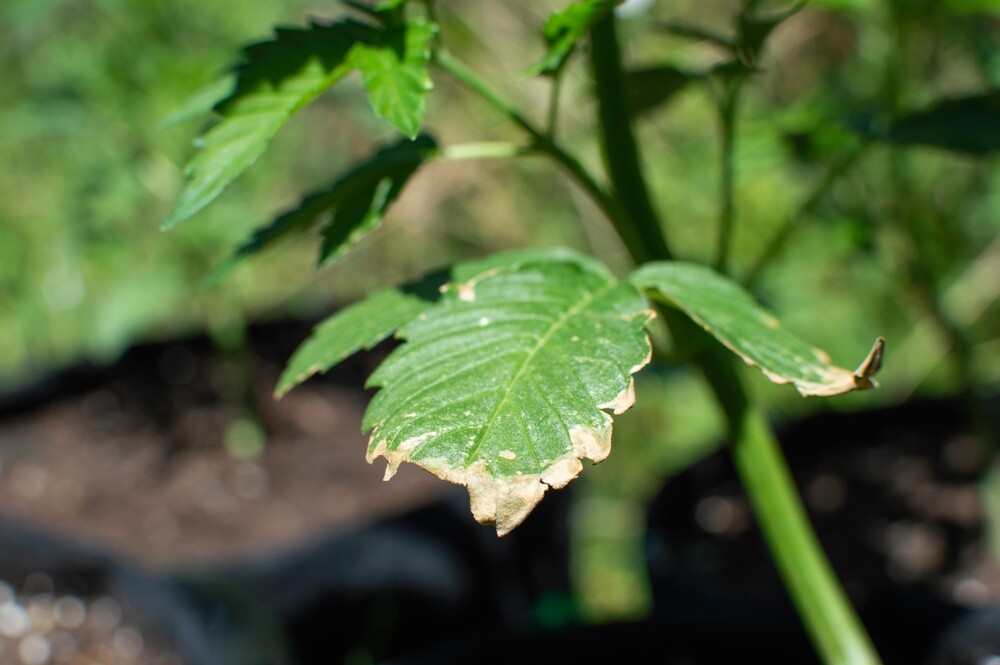

A key point that all novice growers need to understand is that prevention is the best cure. Here are some preventative measures you can take to help avoid potassium deficiency issues ever bugging you:
- Choosing the right soil: Not all soil options are created equal. Choose a high-quality soil with plenty of organic matter and nutrients.
- Using the right fertilizer: Choose a balanced, cannabis specific fertilizer that includes potassium.
- Balanced nutrient feeding: If you are using liquid nutrients, always check your feed water with an EC or TDS meter before feeding.
- Proper watering practices: Overwatering can lead to nutrient deficiencies, so make sure you are watering correctly.
- Regular soil testing: Testing the pH and EC/TDS levels of your soil regularly can make a huge difference to the final outcome. the easiest way to do this is by checking the runoff water after watering/feeding
- Proper watering schedule: Follow a consistent watering schedule that prevents both overwatering and underwatering.
What does too much potassium look like in cannabis?
Excess potassium is just as much of an issue as too little.
Too much potassium can cause toxicity symptoms and lower nutrient absorption. Over-fertilization is the most common cause of excessive potassium levels in cannabis plants.
Symptoms of too much potassium include:
- New fan leaves growing much thinner ‘fingers’ or ‘blades’
- Old fan leaves turning very dark green
- Old fan leaves with burnt ‘crispy’ edges
- Old fan leaves curling downward
FAQs
What causes potassium lockout in cannabis?
Potassium lockout happens when there is an imbalance of other nutrients—like calcium and magnesium. This prevents the plant from absorbing potassium. This can be due to improper pH levels or over-fertilization.
What is a good source of potassium for cannabis plants?
Good sources of potassium include potassium sulfate, kelp meal, greensand, granite dust and wood ash. These can be mixed into the soil or used as part of a nutrient solution.
What is the fastest way to add potassium to your soil?
The quickest way to boost potassium absorption is through water-soluble potassium sulfate. This solution can be directly applied to the soil, ensuring rapid absorption by the plant roots.











